When patients feel better, they live better.
Help your patients get their lives back.
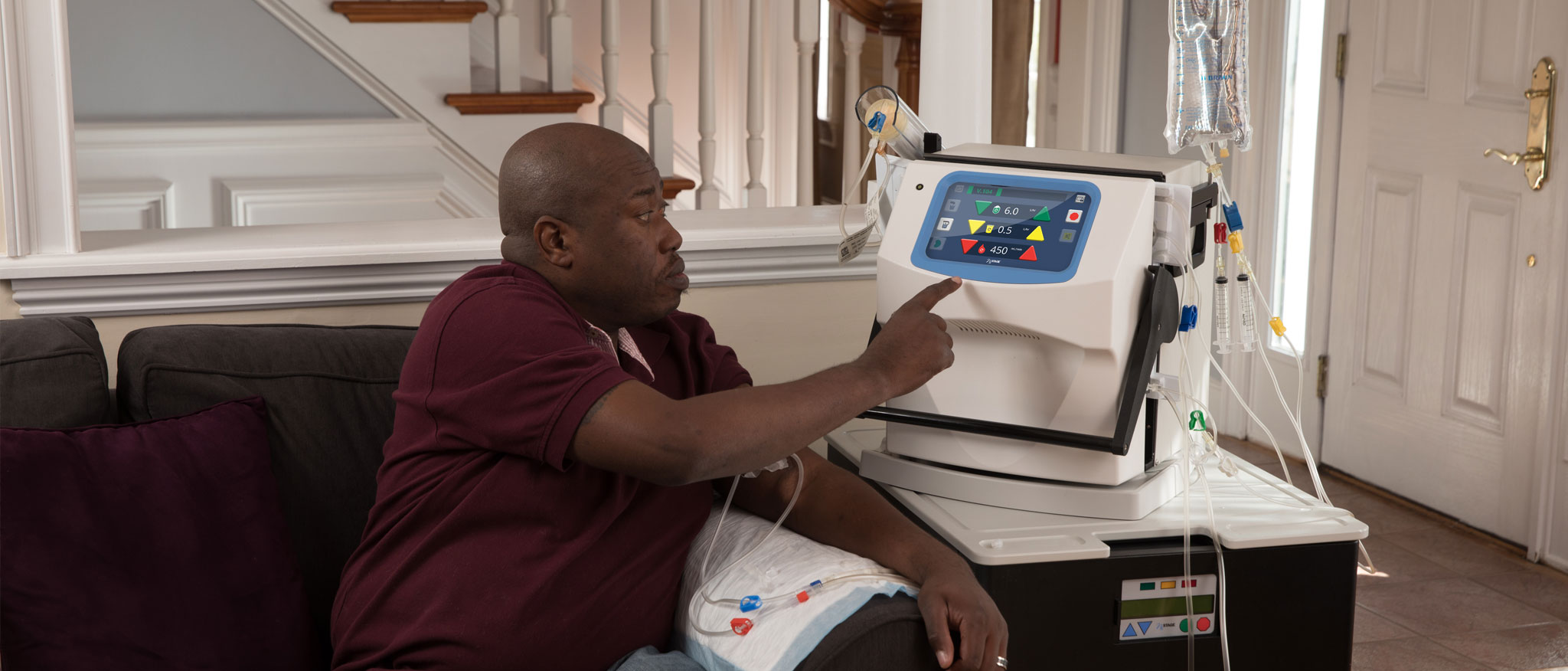
Home hemodialysis (HHD) offers clinicians an opportunity to provide treatments that are uniquely tailored to the individual needs of each patient, taking into consideration their specific clinical and lifestyle needs.
A growing body of evidence supports prescribing more frequent HHD to improve overall outcomes among the growing end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient population, while avoiding the constraints of conventional in-center hemodialysis.1-3
Considerations to Treat the Person, Not Just the Disease
Examples of Thriving HHD Patients and Their Prescriptions
Dialysis is a journey.
ESRD patients typically experience multiple modalities over the course of their disease, which is why it is important to monitor for signs that their current therapy is no longer meeting their clinical and lifestyle needs.
Actual patients not pictured. Patient profiles created from actual home hemodialysis patients. The reported benefits of home hemodialysis may not be experienced by all patients. All forms of hemodialysis involve some risks. See full risks and responsibilities below.

Prior Therapies / Symptoms
- Frequent symptomatic episodes of severe intradialytic hypotension requiring IVF and d/c UF
- Pre-dialysis BP frequently >200/110
- Post-dialysis hypotension
Sample prescription
- Initiated HHD @ 6x/week for 2 hrs/tx
- 15L of dialysate per treatment
- Transitioned to 5x/week for 2.5 hrs/tx to decrease burden of therapy
- 20L of dialysate per treatment
Outcomes
- Normotensive BP
- No left ventricular hypertrophy
- No depressive symptoms
- Traveled to Taiwan twice
Patient has since passed due to causes unrelated to dialysis.

Prior Therapies / Symptoms
- Initially prescribed in-center HD with tunneled dialysis catheter
- Cardiac ischemia and hypotensive during dialysis
- Severe post HD fatigue
- Poor BP control
- Unable to work
- Noncompliant
- Transitioned to PD
- 3.5 years after initiating PD, RRF abruptly declined
- 2 peritonitis episodes within 6 months
Sample prescription
- Initiated HHD @ 5x/week
- 30L of dialysate per treatment
- Transitioned to solo HHD due to loss of care partner
Outcomes
- Afib resolved
- Weight increased from 89kg to 98kg
- Improved activity, sleep, anorexia, and cognitive function

Prior Therapies / Symptoms
- Started ICHD in 1997
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)
- Intermittent AFib
- Severe RLS
- Post-dialysis fatigue
- Reduced muscle mass
- Severe hypertension controlled with 4 medications
- Forced into retirement
- Kidney matched, but clotted venous returns and pulmonary emboli
- Transplant not placed, but IVC filter was
Sample prescription
- Initiated nocturnal HHD 5x/week for 8hrs/tx
- 30L of dialysate per treatment
Outcomes
- No edema or fluid overload
- No LVH
- BP controlled without medication
- Activity remarkably improved and travels as desired
Struggling to manage patients as they transition to hemodialysis?
Learn about how transitional dialysis care can ease patients into dialysis, while educating them on their modality choices.
Home Hemodialysis with NxStage
A Practical Option for More Frequent Therapy
NxStage home hemodialysis products are designed to provide patients with simple, practical options for treatment at home.
NxStage HHD Products
Resources
NxStage is dedicated to supporting healthcare professionals
NxStage offers healthcare professionals with a variety of tools to help with everything from patient selection to prescribing and training.
Supporting healthcare professionals with educational resources from NxStage and third parties, including in-person and online training.
To get an understanding of how our products and therapies can help in your practice, take time to review our clinical evidence library. Our clinical evidence pieces include posters, presentations, and clinical summaries.
Customer Service and Technical Support
24/7 technical support for patients and healthcare professionals
24-hour system swap
Dedicated customer service for inventory management
Nxpeditions patient travel support and delivery program
Contact Us
The reported benefits of home hemodialysis may not be experienced by all patients.
Despite the health benefits that home and more frequent hemodialysis may provide to those with chronic kidney disease, these forms of therapy are not for everyone. Please review this information carefully and discuss it with your doctor as you evaluate your therapy options.
Personal and Partner Responsibility
Home hemodialysis with the NxStage System during the day may not require a care partner, provided a physician and a qualified patient agree that solo home hemodialysis is appropriate. Patients performing nocturnal treatments are required to have a care partner. Care partners are trained on and follow guidelines for proper operation. If you choose to do more frequent home hemodialysis, you will be responsible for complying with your dialysis prescription, which may require treatments up to six days per week.
If you choose to do home hemodialysis alone during the day, you will need to take on the responsibility for tasks that would normally be taken care of by staff when in-center. You will need to perform all aspects of dialysis treatment from start to finish, including equipment setup, needle insertions, responding to and resolving system alarms, and system tear-down after treatment. In addition, you must monitor your blood pressure, ensure proper aseptic technique is followed, and follow all the training material and instructions given to you by your training nurses. You will also be trained on and need to know how to respond to health emergencies that might happen during treatment at home, including dizziness, nausea, low blood pressure, and fluid or blood leaks.
Treatment Environment
You must ensure that you have a clean and safe environment for your treatments. You also need to set aside space in your home for the needed supplies.
Risks Associated with All Forms of Hemodialysis
All forms of hemodialysis involve some risks. These may include high blood pressure, fluid overload, low blood pressure, heart-related issues, vascular access complications, cramps, backache, headache, dizziness, nausea, an “off” taste in the mouth, fatigue, fever, chills, joint pain, itching, seizures or sinusitis.
All hemodialysis therapies also involve the use of medical devices that introduce the potential for additional risks including air entering the bloodstream, damage of red blood cells, inflammatory reactions, blood chemistry imbalances, blood loss due to clotting of the blood tubing set or accidental blood line disconnection or other leak, allergic reactions, and excess warming or cooling of the dialysate. In addition, dialysis patients may have other underlying diseases that may, in some cases, make it more difficult for them to manage their hemodialysis treatments.
Risks associated with More Frequent Home Hemodialysis
Studies suggest that patients performing more frequent home hemodialysis may experience slightly fewer complications associated with their treatments and may experience improved clinical outcomes. However, there are certain risks unique to treatment in the home environment. Treatments at home are done without the presence of medical personnel and on-site technical support. Patients (and their care partners, if required), must both be trained on what to do and how to get medical or technical help if needed. When vascular access is exposed to more frequent use, infection of the site, and other access related complications may also be potential risks.
Risks Associated with Solo Home Hemodialysis Therapy
A qualified patient may dialyze alone, without a care partner present (solo home hemodialysis), provided the patient and physician agree that solo home hemodialysis is appropriate. Certain risks associated with hemodialysis treatment are increased when performing solo home hemodialysis because no one is present to help the patient respond to health emergencies. If patients experience needles coming out, blood loss, or very low blood pressure during solo home hemodialysis, they may lose consciousness or become physically unable to correct the health emergency. Losing consciousness or otherwise becoming impaired during any health emergency while alone could result in significant injury or death. Additional ancillary devices and training are required when performing solo home hemodialysis.
Increased Risks Associated with Home Nocturnal Hemodialysis Therapy
The NxStage System may be used at night while the patient and care partner are sleeping. Certain risks associated with hemodialysis treatment are increased when performing nocturnal therapy due to the length of treatment time and because therapy is performed while the patient and care partner are sleeping. These risks include, but are not limited to, blood access disconnects and blood loss during sleep, blood clotting due to slower blood flow or increased treatment time or both, and delayed response to alarms when waking from sleep. Treatment with nocturnal therapy may require adjustments to medications, including but not limited to iron, Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESA), insulin/oral hypoglycemics, anticoagulants, and phosphate binders.
References
- Weinhandl ED, Nieman KM, Gilbertson DT, Collins AJ. Hospitalization in daily home hemodialysis and matched thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;65(1):98-108.
- Weinhandl ED, Lie J, Gilbertson DT, Arneson TJ, Collins AJ. Survival in daily home hemodialysis and matched thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23(5):895-904.
- Kraus M, Finkelstein FO, Daoui R, et al. Short Daily Hemodialysis (SDHD) improves overall Quality of Life (QOL) and physicial intimacy: interim results from the FREEDOM study. Abstract presented at the American Society of Nephrology Conference, 2011.
- Hall YN, Larive B, Painter P, et al. Effects of six versus three times per week hemodialysis on physical performance, health, and functioning: Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) randomized trials. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(5):782-794.
- Flythe JE, Kimmel SE, Brunelli SM. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular mobidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011;27:250-257.
- Chazot C, Vo-Van C, Lorriaux C. Even a moderate fluid removal rate during individualised haemodialysis session times is associated with decreased patient survival. Blood Purif. 2017;44(2):89-97.
- Daugirdas JT, Blake PG, Ing TS. Handbook of Dialysis. Philidelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins; 2007.
- FHN Trial Group. In-center hemodialysis six times per week versus three times per week. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(24):2287-2300.
- Rocco MV, Lockridge RS, Beck GJ, et al. The effects of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis: the Frequent Hemodialysis Network Nocturnal Trial. Kidney Int. 2011;80(10):1080-1091.
- U.S. Renal Data System, USRDS 2015 Annual Data Report: Table 6.3. Adjusted survival (%) by (a) treatment modality and incident cohort year (year of ESRD onset), and (b) age, sex, race, and primary cause of ESRD, for ESRD patients in the 2008 incident cohort (initiating ESRD treatment in 2008) Abbreviation: ESRD, end-stage renal disease.
- Jaber BL, Lee Y, Collins AJ, et al. Effect of daily hemodialysis on depressive symptoms and postdialysis recovery time: interim report from the FREEDOM (Following Rehabilitation, Economics and Everyday-Dialysis Outcome Measurements) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56(3):531-539.
- Spanner E, Suri R, Heidenheim AP, Lindsay RM. The impact of quotidian hemodialysis on nutrition. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(1 suppl):30-35.
- Finkelstein FO, Schiller B, Daoui R, et al. At-home short daily hemodialysis improves the long-term health-related quality of life. Kidney Int. 2012;82(5):561-569.
- Heidenheim PA, Muirhead N, Moist L, Lindsay RM. Patient quality of life on quotidian hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(S1)(S1):S36-S41.
- Ting GO, Kjellstrand C, Freitas T, Carrie BJ, Zarghamee S. Long-term study of high-comorbidity ESRD patients converted from conventional to short daily hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42(5):1020-1035.
- Goldfarb-Rumyantzev AS, Leypoldt JK, Nelson N, Kutner NG, Cheung AK. A crossover study of short daily haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:166-175.
- Pinciaroli AR. Restuls of daily hemodialysis in Catanzaro: 12-year experience with 22 patients treated for more than one year. Hemodial Int. 1998;2(1):12-17.
- Jaber BL, Schiller B, Burkart JM, et al. Impact of short daily hemodialysis on restless legs symptoms and sleep disturbances. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(5):1049-1056.
- Kraus MA, Cox CG, Summitt CL, et al. Work and travel in a large Short Daily Hemodialysis (SDHD) program. Abstract presented at American Society of Nephrology Annual Conference, 2007.
- Culleton BF, Walsh M, Klarenbach SW, et al. Effect of frequent nocturnal hemodialysis vs conventional hemodialysis on left ventricular mass and quality of life. JAMA. 2007;298(11):1291–1299.
- Pauly RP, Gill JS, Rose CL, et al. Survival among nocturnal home haemodialysis patients compared to kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:2915-2919.
- Ayus JC, Achinger SG, Mizani MR, et al. Phosphorus balance and mineral metabolism with 3 h daily hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2007;71(4):336-342.
- Eloot S, Van Biesen W, Dhondt A, et al. Impact of hemodialysis duration on the removal of uremic retention solutes. Kidney Int. 2008;73:765-770.
- NxStage Medical, Inc. 2018. Quantitative Research Report. Hawk Partners 2017. Assessing Patient Threshold for Solo HHD Risk Tolerance.